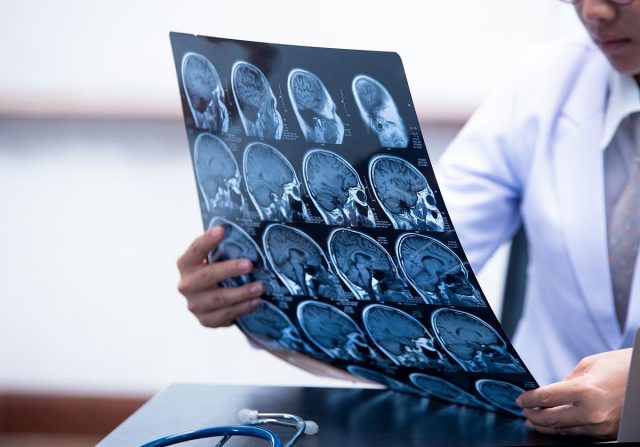
Sensitivity and specificity for CT perfusion and CT angiography as ancillary test for death by neurologic criteria did not meet prespecified validation threshold in recent study
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
THURDAY, June 26, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Neither computed tomography (CT) perfusion nor CT angiography meet the prespecified validation threshold as an ancillary test for death by neurologic criteria (DNC) in critically ill patients, according to a study published online June 13 in JAMA Neurology to coincide with the annual Critical Care Reviews Meeting, held from June 11 to 13 in Belfast, Northern Ireland.
Michaël Chassé, M.D., Ph.D., from the Université de Montréal, and colleagues examined the diagnostic accuracy, interrater reliability, and safety of brain CT perfusion and CT angiography as ancillary investigations for DNC in a prospective, multicenter cohort study conducted in 15 adult intensive care units. Consecutive, critically ill adults with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 3, who were at high risk of DNC, were included.
The primary analysis included 282 patients; 72 percent were ultimately declared deceased by standardized clinical criteria. The researchers found that qualitative brainstem CT perfusion showed sensitivity and specificity of 98.5 and 74.4 percent, respectively; quantitative brainstem CT perfusion was not diagnostically accurate. Qualitative whole-brain CT perfusion yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 93.6 and 92.3 percent, respectively. The sensitivity of CT angiography ranged from 75.5 to 87.3 percent, and specificity varied from 89.7 to 91.0 percent. For all ancillary tests, interrater reliability was excellent (κ ranged from 0.81 to 0.84). Minor, self-limited adverse events occurred in 14 patients; there were no serious adverse events.
“Neither CT perfusion nor CT angiography met the prespecified threshold of greater than 98 percent for both sensitivity and specificity. Consequently, they should not be used as standalone tests to establish DNC,” the authors write.
Several authors disclosed ties to industry; one author reported having multiple related patents.
Copyright © 2025 HealthDay. All rights reserved.