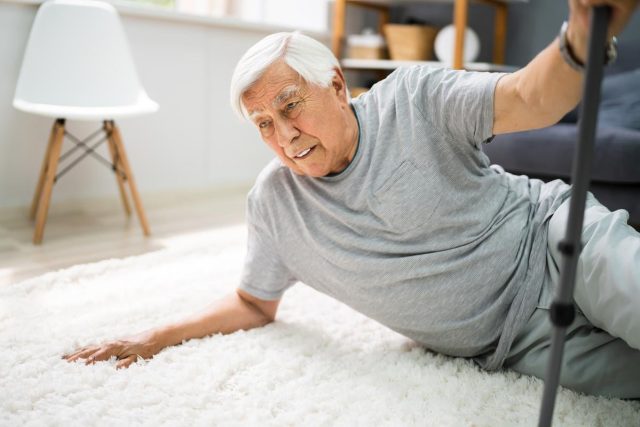
Findings seen in older adults with diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, or fibromyalgia
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
TUESDAY, Jan. 7, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Incident use of gabapentin is not associated with an increase in fall-related hospital visits compared with duloxetine use, according to a study published online Jan. 7 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Alexander Chaitoff, M.D., M.P.H., from the University of Michigan School of Medicine in Ann Arbor, and colleagues describe the risk for fall-related outcomes in older adults with diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, or fibromyalgia starting gabapentin versus duloxetine treatment.
The analytic cohort included 57,086 older adults initiating treatment with gabapentin (52,152 adults) or duloxetine (4,934 adults). The researchers found that the weighted cumulative incidence rates of a fall-related visit at 30, 90, and 180 days were 103.60, 90.44, and 84.44 per 1,000 person-years, respectively, for gabapentin users and 203.43, 177.73, and 158.21 per 1,000 person-years, respectively, for duloxetine users. A lower hazard of falls was seen for incident gabapentin users at six-month follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.52), but no difference was seen in the risk for experiencing severe falls. Across sensitivity and subgroup analyses, the results were similar.
“Incident gabapentin use, compared with incident duloxetine use, was associated with fewer fall-related health care visits and smaller differences in absolute measures and was not associated with an increase in more severe fall-related events,” the authors write. “These considerations should be incorporated into conversations with patients who are considering starting gabapentin treatment.”
Copyright © 2025 HealthDay. All rights reserved.