Residual inflammation significantly linked to higher BMI, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, baseline systemic inflammation
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
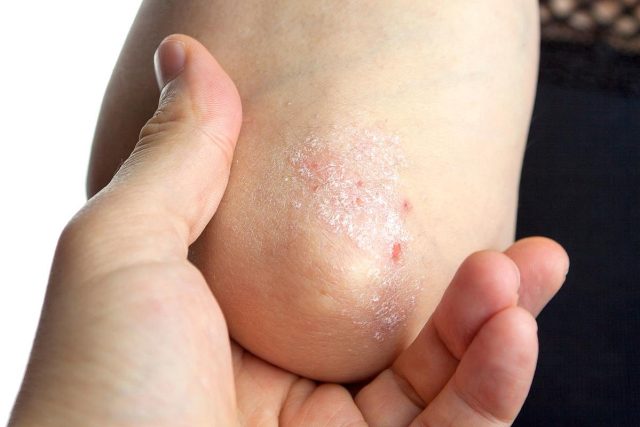
WEDNESDAY, May 21, 2025 (HealthDay News) — For patients with psoriasis receiving biologic therapy, residual inflammation (RI), defined as increased inflammatory markers in blood, characterized by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, despite receiving optimal medical therapy, is observed in about one-third of patients, according to a study published online May 20 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Alba Lecumberri, M.D., from the Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal in Madrid, and colleagues examined RI in patients with psoriasis undergoing biologic therapy in a prospective observational study conducted across three international cohorts. The cohorts included 209 patients with psoriasis who achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of ≤2 after stable biologic therapy.
The researchers found that 36.3 percent of patients had RI, which was significantly associated with higher body mass index, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, increased baseline systemic inflammation, and visceral adipose tissue. In the three cohorts, female sex was a predictor of RI.
“Despite treatment with biologic drugs and adequate skin control, a significant proportion of patients persisted with systemic inflammation, suggesting that nonvisible inflammation may still contribute to cardiovascular risk,” the authors write. “Addressing RI in patients with psoriasis could ultimately lead to more comprehensive treatment strategies aimed at reducing both skin and systemic inflammation.”
Several authors disclosed ties to the biopharmaceutical industry.
Copyright © 2025 HealthDay. All rights reserved.