High triglyceride-glucose index significantly associated with faster cognitive decline in the MCI-Alzheimer disease subgroup
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
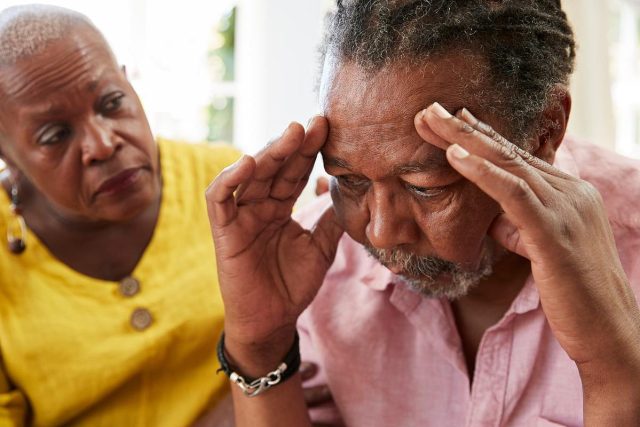
MONDAY, June 30, 2025 (HealthDay News) — For patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) associated with Alzheimer disease (AD), those in the highest tertile of the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index experience faster cognitive decline, according to a study presented at the 11th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology, held from June 21 to 24 in Helsinki.
Bianca Gumina, M.D., from the University of Brescia in Italy, and colleagues conducted a retrospective study to examine insulin resistance (using TyG as a surrogate marker for insulin resistance) as a progression marker in patients with a cerebral spinal fluid-based diagnosis of AD or other neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) who were nondiabetic. Patients were stratified into tertiles according to TyG index (low, medium, high). A total of 315 patients entered the study: 210 with AD and 115 with other NDDs.
The researchers found that high TyG index was linked to worse blood-brain-barrier markers in AD and interacted with APOE ε4, with no effect seen in other NDDs. More cardiovascular risk factors were exhibited in patients with AD with high TyG index, while baseline characteristics were similar. In the MCI-AD subgroup (161 patients), high TyG index was significantly associated with faster cognitive decline over three years of follow-up (hazard ratio, 4.08). For MCI-to-dementia conversion, there was a similar but nonsignificant trend observed. For progression, there was no significant TyG index-APOE interaction. In the other NDDs group, TyG index showed no impact on clinical progression.
“We were surprised to see the effect only in the Alzheimer’s spectrum and not in other neurodegenerative diseases,” Gumina said in a statement. “It suggests a disease-specific vulnerability to metabolic stress during the prodromal window, when interventions may still change the trajectory.”
Abstract No. OPR-066
Copyright © 2025 HealthDay. All rights reserved.